Custodial vs. Non-Custodial Crypto Wallets: What's the Difference?
- AI summary
- Key Facts About Custodial and Non-Custodial Wallets
- How Do Cryptocurrency Wallets Work?
- What Is a Custodial Wallet?
- Why Custodial Wallets Are Popular
- What Is a Non-Custodial Wallet?
- Self-Custodial vs. Non-Custodial Wallets: Is There a Difference?
- Custodial vs. Non-Custodial Wallets: Comparison Table
- Security Tips for Using Custodial Wallets
- Which Crypto Wallet Should You Use?
- Final Thoughts: Custodial vs. Non-Custodial Wallets
AI summary
The article explains the key differences between custodial and non-custodial cryptocurrency wallets. Custodial wallets are managed by third parties, offering user-friendly features and account recovery but requiring users to trust the provider with their assets, while non-custodial wallets give users full control and ownership of their private keys, offering greater privacy and independence but demanding more responsibility for security and backups. The choice between wallet types depends on individual preferences for control, convenience, and risk tolerance, with strong security practices being essential for both.
Imagine your crypto assets as valuable treasures locked inside a digital vault. The way that the vault is protected and accessed depends on the type of crypto wallet you use. Custodial wallets work like traditional banks. A third party holds your assets and manages your private keys for you. Non-custodial wallets, by contrast, put you entirely in control by giving you sole ownership of your private keys. Understanding the difference between custodial and non-custodial wallets is essential if you want to choose the right option for your goals, experience level, and risk tolerance.
Key Facts About Custodial and Non-Custodial Wallets
- Third-party providers manage custodial wallets and control your private keys.
- A standard Coinbase account is an example of a custodial wallet
- Non-custodial wallets give you complete control over your crypto assets
- Popular non-custodial wallets include MetaMask, Trust Wallet, and hardware wallets like Tangem
- Both wallet types come with clear advantages and trade-offs
How Do Cryptocurrency Wallets Work?
A cryptocurrency wallet is a software or hardware tool that allows you to interact with a blockchain network. Wallets do not actually store crypto assets. Instead, they store the cryptographic keys needed to access and manage them on the blockchain.
Every crypto wallet has two core components:
- Public Keys and Wallet Addresses: Your public key generates wallet addresses that others can use to send cryptocurrency to you. These addresses are visible on the blockchain and can be shared safely.
- Private Keys: Your private key is what gives you control over your assets. It signs transactions and proves ownership of your funds. Anyone with access to your private key can access your crypto, which is why protecting it is critical.
Wallets can exist in various forms, including mobile apps, desktop software, browser extensions, hardware devices, or even paper backups. Many wallets also support NFTs in addition to cryptocurrencies.
What Is a Custodial Wallet?
A custodial wallet is a crypto wallet where a third party controls your private keys and holds your assets on your behalf. This third party is usually a centralized exchange or financial service provider.
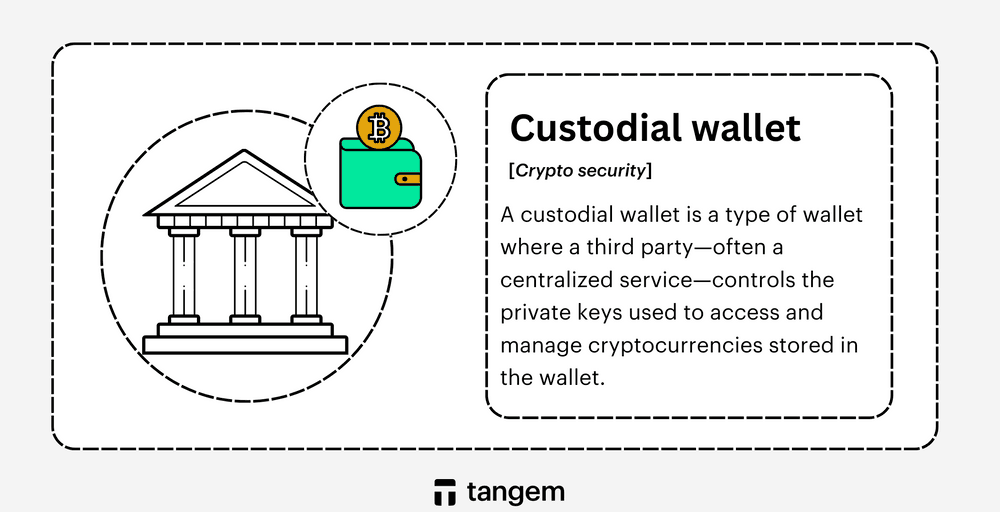
When you use a custodial wallet, you rely on the provider to secure your funds, approve transactions, and handle account recovery.
Why Custodial Wallets Are Popular
Custodial wallets are popular because they reduce the burden of personal responsibility. If you forget your password or lose access, customer support can often assist you in recovering your account. They also simplify inheritance and asset access since the provider maintains custody. The setup helps prevent situations where funds are permanently lost because no one ever shared the private key.
However, using a custodial wallet means trusting a third party with your assets. That makes it essential to choose a regulated, reputable provider and understand how they store keys, as well as whether insurance coverage is in place.
What Is a Non-Custodial Wallet?
A non-custodial wallet is a crypto wallet where only you control the private keys. No third party can access or manage your funds. Non-custodial wallets are ideal for users who want full ownership and direct interaction with blockchains and decentralized applications.
You need them to use decentralized exchanges such as Uniswap, SushiSwap, PancakeSwap, and QuickSwap. Popular non-custodial wallet providers include MetaMask, Trust Wallet, and Tangem. With these wallets, you are solely responsible for protecting your seed phrase and private keys.
Self-Custodial vs. Non-Custodial Wallets: Is There a Difference?
There is no difference. The terms self-custodial, non-custodial, self-hosted, and self-sovereign wallets all describe the same concept.
What Is a Self-Custodial Wallet?
A self-custodial wallet grants you complete control over your private keys and crypto assets, eliminating the need for a third-party intermediary.
Hardware wallets, such as Tangem, and paper wallets are common examples. People consider these wallets highly secure when they follow best practices, but they also require careful handling and regular backups to maintain their security.
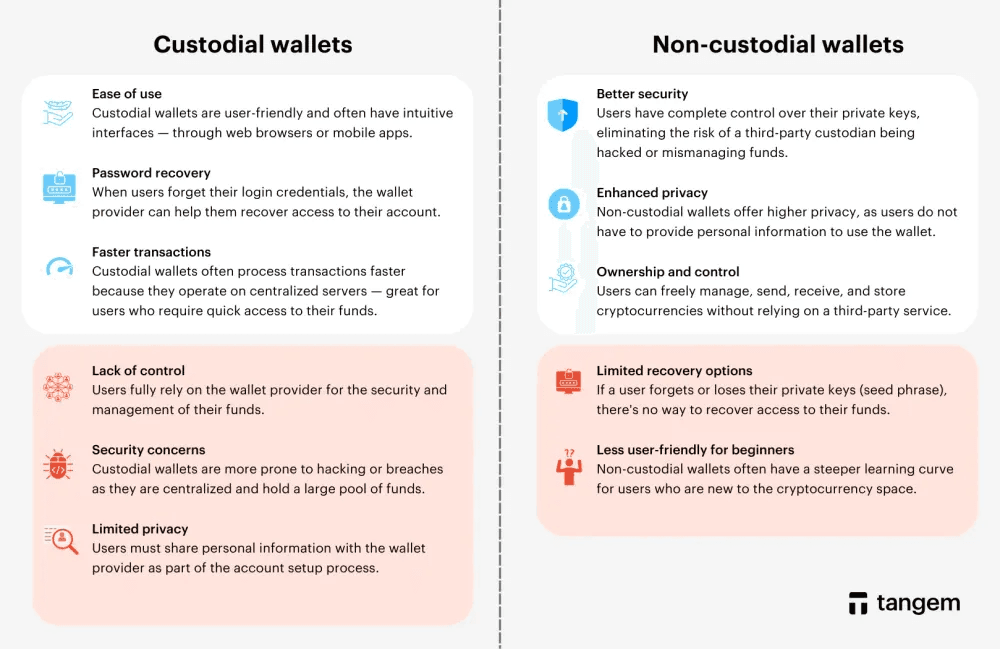
Disadvantages of Custodial Wallets
The biggest drawback of custodial wallets is loss of control. Since a third party holds your private keys, you face risks such as:
- Exchange hacks and security breaches
- Account freezes or withdrawal limits
- Mandatory identity verification and reduced privacy
If you use custodial wallets, choose providers that adhere to strong security standards, comply with relevant regulations, and maintain transparent custody practices.
Advantages of Non-Custodial Wallets
- Full ownership of your crypto assets
- No reliance on third parties
- Faster access to funds without withdrawal approval
- Lower fees with no custodial charges
- Greater privacy
Disadvantages of Non-Custodial Wallets
- Less beginner-friendly
- No customer support for lost keys
- Full responsibility for backups and recovery
Non-custodial wallets reward good security habits, but they offer no safety net if you make a mistake.
Custodial vs. Non-Custodial Wallets: Comparison Table
Feature | Custodial Wallets | Non-Custodial Wallets |
Control | Third-party controls keys | User controls the key |
Security | Depends on the provider | Depends on user practices |
Ease of Use | Very user-friendly | Requires technical understanding |
Backup | Managed by the provider | User-managed |
Recovery | Provider may assist | User-only responsibility |
Privacy | Limited due to KYC | Higher privacy |
Regulation | Often regulated | User choice |
Hack Risk | Centralized target | Reduced centralized risk |
Examples | Coinbase, Binance, Kraken | Tangem, MetaMask, Trust Wallet |
Security Tips for Using Custodial Wallets
If you choose a custodial wallet, protect yourself by:
- Using strong, unique passwords
- Enabling multi-factor authentication
- Staying alert for phishing scams
- Avoiding suspicious links and downloads
Which Crypto Wallet Should You Use?
Both custodial and non-custodial wallets can store cryptocurrencies and NFTs. Many users rely on both, using custodial wallets for trading and non-custodial wallets for long-term storage and DeFi access. Always confirm that your chosen wallet supports the specific tokens and blockchain networks you plan to use.
Final Thoughts: Custodial vs. Non-Custodial Wallets
There is no single best crypto wallet for everyone. The right choice depends on how much control, responsibility, and independence you want. If you value convenience and account recovery, a custodial wallet may be a suitable option for you. If you wish to have full ownership and self-sovereignty, Tangem, a non-custodial wallet, is the better option. Regardless of which option you choose, staying informed and following strong security practices is the most crucial step in protecting your cryptocurrency assets.